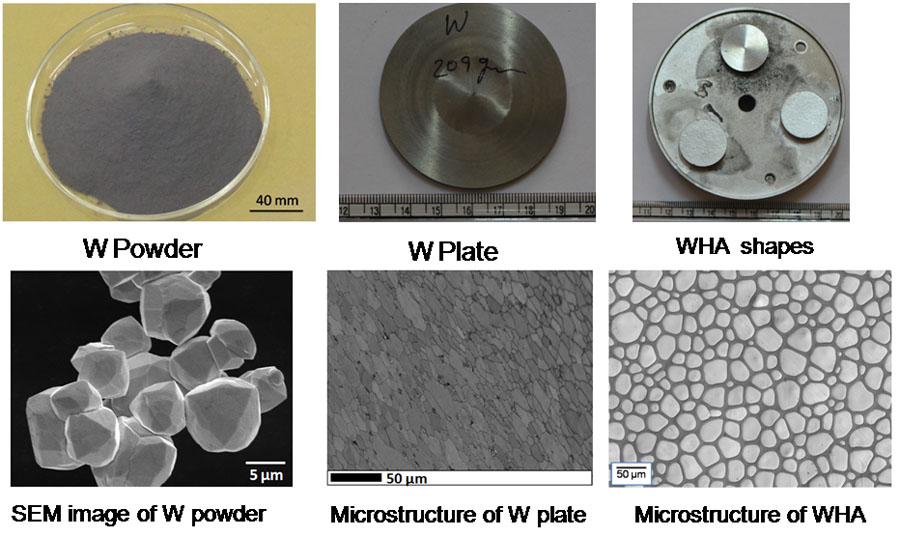
Tungsten is a strategically important metal. It has high melting point, high density and superior mechanical strength at high temperatures. Tungsten has a wide range of applications cutting tools (cemented carbide tools), high speed steels, plasma facing components etc. Tungsten based heavy alloys (WHA) such as W-Ni-Fe and W-Ni-Cu possess distinguished properties with respect to absorbing radiation, mechanical strength and machinability. These are the ideal materials for a wide range of applications, such as in aerospace, military, the automotive industry, medical engineering and the construction industry.
Tungsten is a strategically important metal. It has high melting point (3410°C), high density (19.26 g/cc) and superior mechanical strength at high temperatures. Tungsten metal is being considered to be used as plasma facing components of fusion reactors (ITER). Tungsten based heavy alloys (WHA) such as W-Ni-Fe and W-Ni-Cu possess distinguished properties with respect to absorbing radiation, mechanical strength and machinability. These are the ideal materials for a wide range of applications, such as in aerospace, the automotive industry, medical engineering and the construction industry. Pure tungsten is also used as an alloying element in various grades of steels and nickel based alloys.
Tungsten is a strategically important metal. It has high melting point (3410°C), high density (19.26 g/cc) and superior mechanical strength at high temperatures. Tungsten metal is being considered to be used as plasma facing components of fusion reactors (ITER). Tungsten based heavy alloys (WHA) such as W-Ni-Fe and W-Ni-Cu possess distinguished properties with respect to absorbing radiation, mechanical strength and machinability. These are the ideal materials for a wide range of applications, such as in aerospace, the automotive industry, medical engineering and the construction industry. Pure tungsten is also used as an alloying element in various grades of steels and nickel based alloys.