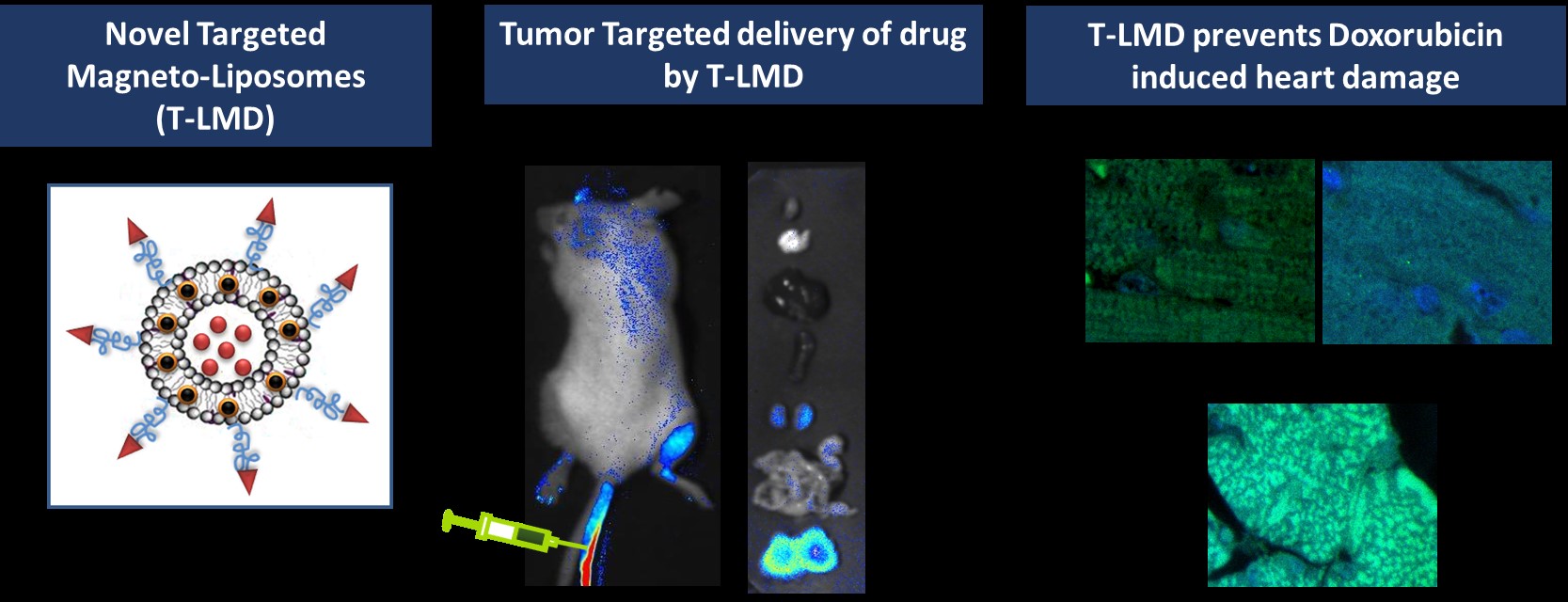
The current technology relates to the design and synthesis of a novel magneto-liposomal nano-formulation of Doxorubicin (DOX), referred to as ‘T-LMD’. As compared to commercially available liposomal nano-formulation of DOX, T-LMD shows ~ 3 folds better anti-cancer efficacy in fibrosarcoma, glioblastoma, lung carcinoma and triple negative breast carcinoma cancer cells. Furthermore, in combination with gamma radiation, T-LMD acts as a radio-sensitizer further increasing the tumor killing efficacy by ~ 3 folds as compared to commercial liposomal DOX nano-formulation.
T-LMD causes enhanced tumor killing due to following reasons:
Chemo-radiotherapy is the most commonly used cancer treatment modality in India and abroad. However conventional chemo-radiotherapy suffers the limitation of non-specificity, resulting in damage to cancer as well as normal cells. Nanotechnology has been making leaps of progress in improving the efficacy and reducing the side effects of chemo-radiotherapy. Thus, BARC has developed novel targeted magneto-liposomal nanoparticles, called as T-LMD, that can deliver doxorubicin chemotherapy to cancer cells, especially fibrosarcoma and triple negative breast carcinoma in a targeted manner and significantly reduce the doxorubicin induced cardiac toxicity. Moreover, this T-LMD nanoparticles can increase the gamma radiation induced DNA double strand breaks in cancer cells. AT BARC, we have robustly tested the tumor targeted delivery and anti-cancer efficacy of T-LMD nanoparticles for improvement of chemo-radiotherapy efficacy in mice tumor models. The developed T-LMD holds potential for clinical application in cancer patients as an anti-cancer formulation in combination with radiotherapy after generating required pre-clinical/clinical data and regulatory approval. The design and applications of T-LMD has received an Indian Patent (No. 441803).
Liposomal doxorubicin, is clinically used as a mainstream chemotherapy agent for treatment of metastatic breast cancer, ovarian cancer and sarcomas. However, the anti-tumor efficacy of liposomal doxorubicin can be further improved by enhancing its tumor targeting ability, increasing its anti-tumor efficacy and substantially reducing the doxorubicin associated side effects, specifically to the heart, kidneys and liver. Herein, we have developed a novel tumor targeted liposomal nano-formulation of doxorubicin, called as ‘T-LMD’ and demonstrated its superior tumor targeting ability in mice tumor models. Moreover, T-LMD showed negligible accumulation in the heart of mice post-intravenous administration and subsequently resulted in negligible toxicity to the heart in healthy mice. The T-LMD nano-formulation has been co-encapsulated with iron oxide nanoparticles which significantly increase its anti-tumor efficacy by 2-3 folds when used as a chemotherapy agent. In combination with gamma radiation therapy, T-LMD significantly sensitizes the mice tumors to radiation induced cell killing resulting in further 3 fold enhancement of tumor killing efficacy as compared to clinically used liposomal doxorubicin nano-formulation. T-LMD showed significant potential to improve the chemo-radiotherapy efficacy of doxorubicin in case of fibrosarcoma and triple negative breast carcinoma with significant prevention of the doxorubicin associated toxicity to normal organs, such as heart, liver and kidneys in mice tumor models. T-LMD is likely to show efficacy in other cancer types to be tested.