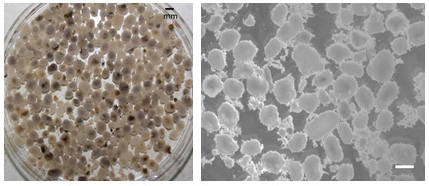
The hybrid Granular SBR Treatment (GST) is a compact biological treatment method for effective removal of contaminants from domestic and industrial wastewaters. It makes use of the natural microbes present in the wastewater for removing contaminants. The microbial growth is predominantly in bio-beads comprising of biomass particles (biofilms and granules). Bio-beads (i) achieve high biomass levels, (ii) simplify separation of biomass from treated wastewater and (iii) decrease the load of pollutants to acceptable levels. The bio-beads produced during wastewater treatment are a source of C, N and P and a fertilizer-supplement in organic farming. The value of the resources recovered from wastewater treatment plants i.e. treated wastewater and fertilizer-supplement, can partly recover the OPEX. The GST uses the unique features of sequencing batch reactor (SBR) and bio-beads for treating wastewater in a single tank system without secondary clarifiers. It enables building compact effluent and sewage treatment plants with smaller land footprint and lower costs as compared to other methods. This process does not involve chemical addition for removing nutrients & provides odour free sewage treatment plants.
The hybrid Granular SBR Treatment (GST) is a compact biological treatment method for effective removal of contaminants from domestic and industrial wastewaters. It makes use of the natural microbes present in the wastewater for removing contaminants. The bacterial growth is predominantly in bio-beads comprising of biomass particles (biofilms and granules). Bio-beads (i) achieve high biomass levels, (ii) simplify separation of biomass from treated wastewater and (iii) decrease the load of pollutants to acceptable levels. The bio-beads produced during wastewater treatment are a source of C, N and P and a fertilizer-supplement in organic farming. The value of the resources recovered from wastewater treatment plants i.e. treated wastewater and fertilizer-supplement can partly recover the OPEX.
The hybrid Granular SBR Treatment (GST) is a compact biological treatment method for effective removal of contaminants from domestic and industrial wastewaters. It makes use of the natural microbes present in the wastewater for removing contaminants. In this process, microbial growth is predominantly in bio-beads comprising of biomass particles (biofilms and granules). Bio-beads (i) achieve high biomass levels, (ii) simplify separation of biomass from treated wastewater and (iii) decrease the load of pollutants to acceptable levels. The bio-beads produced during wastewater treatment are a source of C, N and P and a fertilizer-supplement in organic farming. The value of the resources recovered from wastewater treatment plants i.e. treated wastewater and fertilizer-supplement, can partly recover the OPEX involved in running the plant.
Process conditions are conducive for selecting and enriching functional, aggregating and slow-growing microbes in bio-beads. Bio-beads are formed from natural microbes present in the wastewater. It is the most natural way of forming bio-beads and treating wastewater. Each batch of treatment comprises of time-gated steps such as filling, mixing, settle and decant phases. Reaction phase is distributed amongst anaerobic and aerobic steps. The length of each batch cycle and individual phases depends on type of wastewater, its characteristics and effluent quality requirements. The GST uses familiar sequencing batch reactor (SBR) technology for treating wastewater. SBR is a proven technology for small, medium and large scale wastewater treatment plants. Multiple SBR tanks facilitate to achieve continuity in large volume wastewater treatment plants.
Sewage Treatment using pilot-scale GST
| Parameters | Influent | Effluent |
|---|---|---|
| COD (mg/l) | 200 - 600 | <10 |
| BOD5 (mg/l) | 250 | <10 |
| TN (mg/l) | 15 - 30 | <5 |
| TP (mg/l) | 3 – 6 | <2 |
| TSS (mg/l) | Up to 170 | <30 |